food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome treatment
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome can be included under Asatmyaja-rogas one which is not conducive to the prakrithi constitution and agni digestive fire of a particular person. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypothermia hypotension and metabolic derangements.

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table
Avoidance of triggering foods ensuring good nutrition healing the gut balancing the immune system and maintaining a good inflammatory balance are keys to treatment.

. Symptoms include severe vomiting and. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in.
We aim to review the recent literature and to provide an update on diagnosis and management of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES and food protein-induced allergic. We review here the peculiar. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system.
If a severe reaction does occur. About Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract.
Like other food allergies. Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that was previously thought to only affect infants and.
Why Starting Solids Early Will Not Help Your Baby Gain Weight with Rosan Meyer PhD RD. Symptoms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can vary from child to child and in severity. FPIES usually develops in infancy and resolves around 3-5 years of age.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome Symptoms. Prevention and Management The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet. In the last years the interest of the scientific community toward food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES has grown exponentially.
The term protein refers to large biological molecules composed of amino acids. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting. Episode 110 Catch-Up Weight.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a rare disorder mostly affecting infants 0-3 years and young children 3-10 years which occurs when foods that. Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. Changes in blood pressure and body temperature.
Diarrhea that begins after vomiting. FPIES food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome is a serious allergic reaction to certain foods. Other episodes mentioned.
The principal suggested treatments. FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is. Adults and children have different experiences with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome although more research is necessary according to a study published.
To read and learn more. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. Clinical management food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome oral food challenge INTRODUCTION The clinical management of a patient who has.

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect
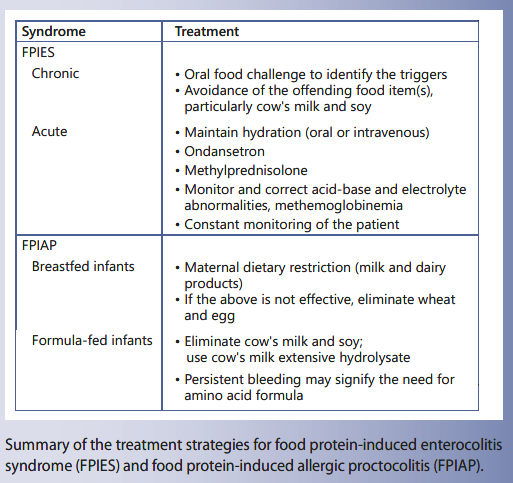
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
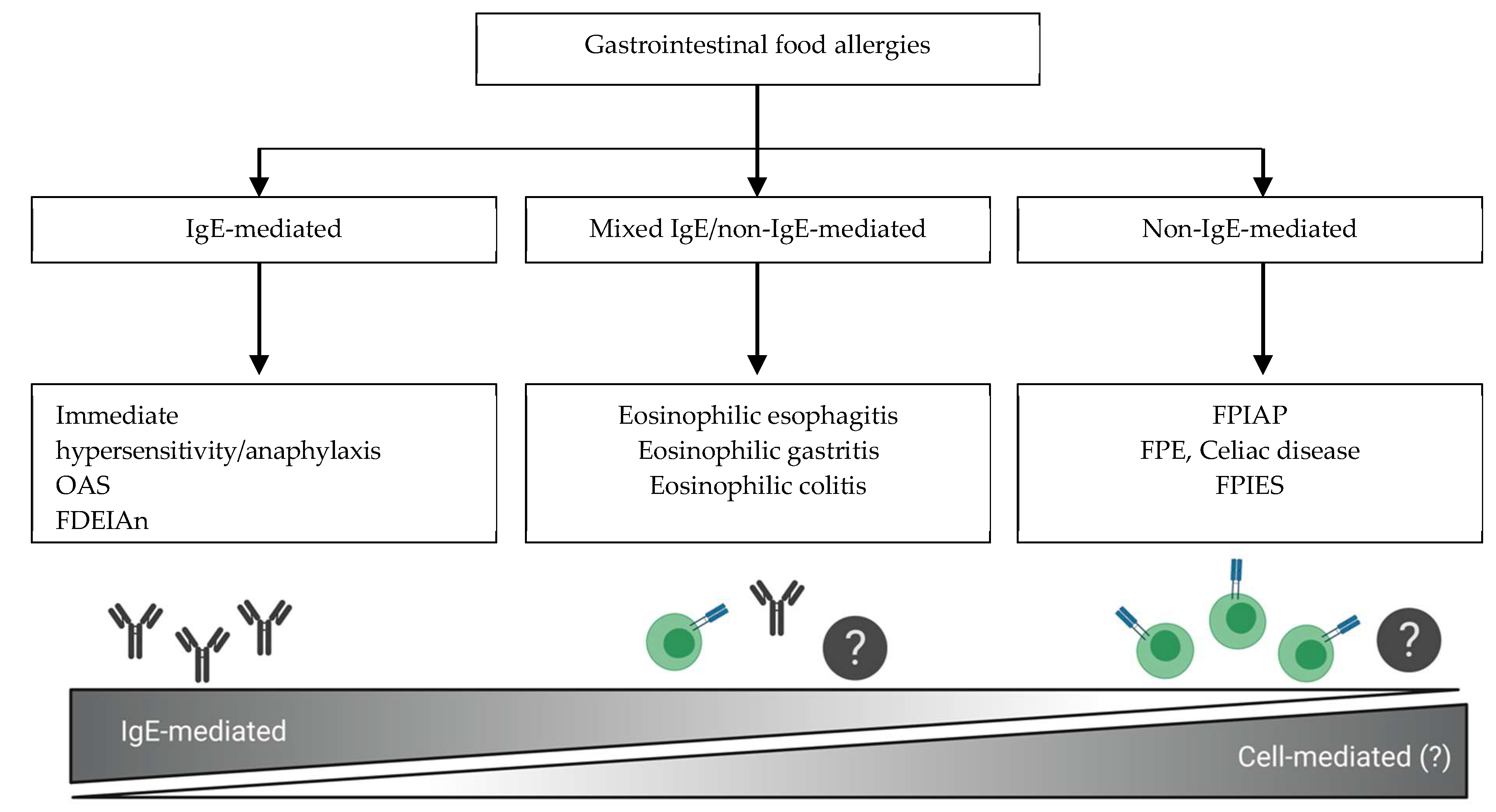
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Comparison Between Acute And Chronic Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram

Algorithm For The Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Tweets With Replies By Eastmidsfoamed Em3foamed Twitter

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Description Of Differences And Similarities Between Fpies Fpe And Download Scientific Diagram
